Server Man
Well-Known Member
- May 17, 2015

- Windows 10

- Chrome 67.0.3396.99
One of the important security management responsibilities of Microsoft Intune is the ability to issue certificates to devices using the Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP). SCEP is an industry standard protocol implemented by most certification authorities to simplify large scale certificate issuance. We are pleased to announce Intune support for SCEP request validation using third-party certification authorities. Entrust Datacard is the first Microsoft partner solution to support this interoperability.
Digital certificates have become increasingly popular to identify a user or device before granting access to corporate resources such as Wi-Fi and VPN access, web applications, and cloud storage. They are also used to encrypt and sign email, so recipients know they can trust the sender and only the intended recipients can read the message. Certificate-based authentication prevents untrusted devices (devices without certificates issued from a trusted source) from accessing the network, which is important with widespread use of bring-your-own-device (BYOD) and corporate-owned mobile devices in the modern workplace. Some of these devices may belong to external partners (contractors, vendors, temporary workers) who have legitimate requirement to access the corporate network but appear as unknown devices to the organization. To protect against ever-increasing and ever more sophisticated attacks, IT must ensure not only the right user has access to the right databut that they’re also using the right device.
Digital certificates allow IT to embed a trusted identity onto users’ mobile devices, with little to no change in user behavior. They enable a transparent and frictionless authentication experience, so users dont have to enter domain credentials such as username and password to seek access each time. Intune provides a set of APIs that allow third-party certificate authorities to interoperate with our certificate delivery capabilities utilizing the SCEP protocol. Using these supported platforms, Intune admins may execute tasks such as issue certificates to new employees, renew certificates, and control which users and devices can access applications and networks.
In the context of mobile devices, certificate requests are generally initiated by the device after receiving a certificate profile from Intune.Figure 1 below describes a simplified workflow of how Intunes SCEP solution securely delivers certificates. Intune generates a dynamic challenge and some additional integrity check information, which is then encrypted and sent to the device. The integrity check information is used to ensure the integrity of the certificate issuance process, by making sure the subject, SAN, and other fields in the certificate signing request (CSR) received by SCEP server match the information in Intune. When the device reaches out to the SCEP server with the CSR and challenge, Intune validates the integrity of the CSR and dynamic challenge before the certificate is issued by the SCEP server.
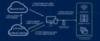
Figure 1. Workflow summary for Intune SCEP certificate validation.
Like previously supported Active Directory Certificate Services, the new Intune and Entrust Datacard interoperability ensures no tampering occurs at any point in the certificate issuance process while using SCEP. Organizations can issue certificates via Entrust Datacard to provide seamless authentication to applications and on-premises resources, creating a user-friendly, flexible, and cost-effective experience. In addition to certificate-based authentication, Microsoft and Entrust will add support for other capabilities and scenarios, such as modern provisioning, secure email, and data protection. Microsoft engineers are also collaborating with other public key infrastructure (PKI) and certificate management providers to integrate their solutions with Intunes SCEP validation API.
Device certificates add an important layer of security for organizations adopting a modern workplace powered by Microsoft 365, including Intune, Azure Active Directory, and Office 365. It will be rolled out for general availability later this quarter.
To learn more, contact your Microsoft and Entrust representatives, and review the documentation.
Continue reading...
Digital certificates have become increasingly popular to identify a user or device before granting access to corporate resources such as Wi-Fi and VPN access, web applications, and cloud storage. They are also used to encrypt and sign email, so recipients know they can trust the sender and only the intended recipients can read the message. Certificate-based authentication prevents untrusted devices (devices without certificates issued from a trusted source) from accessing the network, which is important with widespread use of bring-your-own-device (BYOD) and corporate-owned mobile devices in the modern workplace. Some of these devices may belong to external partners (contractors, vendors, temporary workers) who have legitimate requirement to access the corporate network but appear as unknown devices to the organization. To protect against ever-increasing and ever more sophisticated attacks, IT must ensure not only the right user has access to the right databut that they’re also using the right device.
Digital certificates allow IT to embed a trusted identity onto users’ mobile devices, with little to no change in user behavior. They enable a transparent and frictionless authentication experience, so users dont have to enter domain credentials such as username and password to seek access each time. Intune provides a set of APIs that allow third-party certificate authorities to interoperate with our certificate delivery capabilities utilizing the SCEP protocol. Using these supported platforms, Intune admins may execute tasks such as issue certificates to new employees, renew certificates, and control which users and devices can access applications and networks.
In the context of mobile devices, certificate requests are generally initiated by the device after receiving a certificate profile from Intune.Figure 1 below describes a simplified workflow of how Intunes SCEP solution securely delivers certificates. Intune generates a dynamic challenge and some additional integrity check information, which is then encrypted and sent to the device. The integrity check information is used to ensure the integrity of the certificate issuance process, by making sure the subject, SAN, and other fields in the certificate signing request (CSR) received by SCEP server match the information in Intune. When the device reaches out to the SCEP server with the CSR and challenge, Intune validates the integrity of the CSR and dynamic challenge before the certificate is issued by the SCEP server.
Figure 1. Workflow summary for Intune SCEP certificate validation.
Like previously supported Active Directory Certificate Services, the new Intune and Entrust Datacard interoperability ensures no tampering occurs at any point in the certificate issuance process while using SCEP. Organizations can issue certificates via Entrust Datacard to provide seamless authentication to applications and on-premises resources, creating a user-friendly, flexible, and cost-effective experience. In addition to certificate-based authentication, Microsoft and Entrust will add support for other capabilities and scenarios, such as modern provisioning, secure email, and data protection. Microsoft engineers are also collaborating with other public key infrastructure (PKI) and certificate management providers to integrate their solutions with Intunes SCEP validation API.
Device certificates add an important layer of security for organizations adopting a modern workplace powered by Microsoft 365, including Intune, Azure Active Directory, and Office 365. It will be rolled out for general availability later this quarter.
To learn more, contact your Microsoft and Entrust representatives, and review the documentation.
Continue reading...